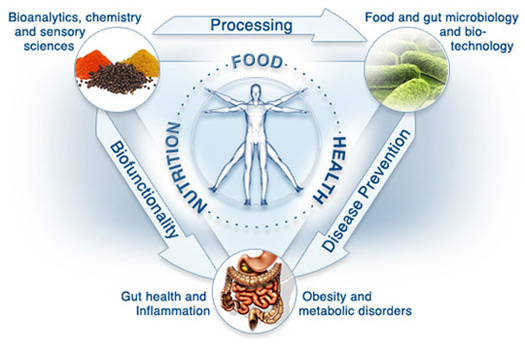
Functional Nutritional Medicine
Emphasizes the importance of high quality foods and phytonutrient
diversity to address clinical imbalances and move individuals toward the highest
expression of health. By addressing root cause, rather than symptoms, clinical functional
nutritional medicine practitioners become oriented to identifying the complexity of disease.
One condition has many different causes and, likewise, one cause may result in many
different conditions. Nutritional Medicine is an. It requires a detailed understanding of each
patient’s genetic, biochemical, and lifestyle to direct personalised treatment plan that leads to improved patient outcomes.
Advanced nutrition assessment and a thorough Functional Medicine based history leads to a personalized therapeutic intervention created to promote optimal health and prevent diet and lifestyle-related disease.
Nutrition is the core modality of Functional Nutritional Medicine, an integrative approach to health. “Functional Nutritional Medicine is an evolution in the practice of medicine that better addresses the healthcare needs of the 21st century. By shifting the traditional disease-centered focus of medical practice to a more patient-centered approach.
Functional Nutritional Medicine addresses the whole person, not just an isolated set of symptoms. Functional Medicine practitioners spend time with their patients, listening to their histories and evaluating the interactions among genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors that can influence long-term health and complex, chronic disease. In this way, Functional Medicine supports the unique expression of health and vitality for each individual.”
Prevention is paramount. Virtually every complex, chronic disease is preceded by long-term disturbances in functionality that can be identified and effectively managed
Functional Medicine expands the clinician’s tool kit. Treatments may include combinations of drugs, botanical medicines, nutritional supplements, therapeutic diets, or detoxification programs. They may also include counseling on lifestyle, exercise, or stress-management techniques.
The patient becomes a partner. As a patient, you become an active partner with your Functional Medicine practitioner. Such a partnership allows you to be in charge of improving your own health and changing the outcome of disease.
Functional Medicine practitioner is able to understand how your body
- rids itself of toxins
- regulation of hormones and neurotransmitters
- immune system function
- digestion and absorption of nutrients and the health of the digestive tract
- structural integrity
- psychological and spiritual equilibrium
- how you produce energy inflammatory responses
 INGREDIENTS
INGREDIENTS
 Ingredients
Ingredients
